golang
Golang 跨平台编译参数
//1、Mac下编译Linux, Windows平台的64位可执行程序
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=windows GOARCH=amd64 go build
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=windows GOARCH=386 go build //32位运行程序
//2、Linux下编译Mac, Windows平台的64位可执行程序
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=darwin GOARCH=amd64 go build
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=windows GOARCH=amd64 go build
//3、Windows下编译Mac, Linux平台的64位可执行程序
SET CGO_ENABLED=0 SET GOOS=darwin3 SET GOARCH=amd64 go build
SET CGO_ENABLED=0 SET GOOS=linux SET GOARCH=amd64 go build
//4、编译arm 64位可执行程序
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux GOARCH=arm64 go build -o ./uuapk/classified-arm@v1.0.0.51 main.go
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o ./uuapk/sursen-admin@v1.0.1.99 main.go
//5、压缩编译
CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux GOARCH=arm64 go build -trimpath -ldflags="-s -w" -o ./uuapk/sursen-admin@v1.0.5.12-arm64-co main.go
Homebrew 方式
go版本升级,降级,切换等
#先升级brew
brew update
#搜索可安装的go版本列表
brew search go
# 安装 指定版本的go
brew install [email protected]
# 取消 go 与之版本的链接
brew unlink go
# 与新装的 go 版本建立链接
brew link --force [email protected]
#刷新下配置文件
source ~/.bash_profile
手动下载 方式
2.安装pkg文件
3.查看是否安装成功 go version
4.查看安装位置 whereis go
5.查看go 环境 go env
Go方式升级
go install golang.org/dl/go1.20@latest
Go一些常见问题
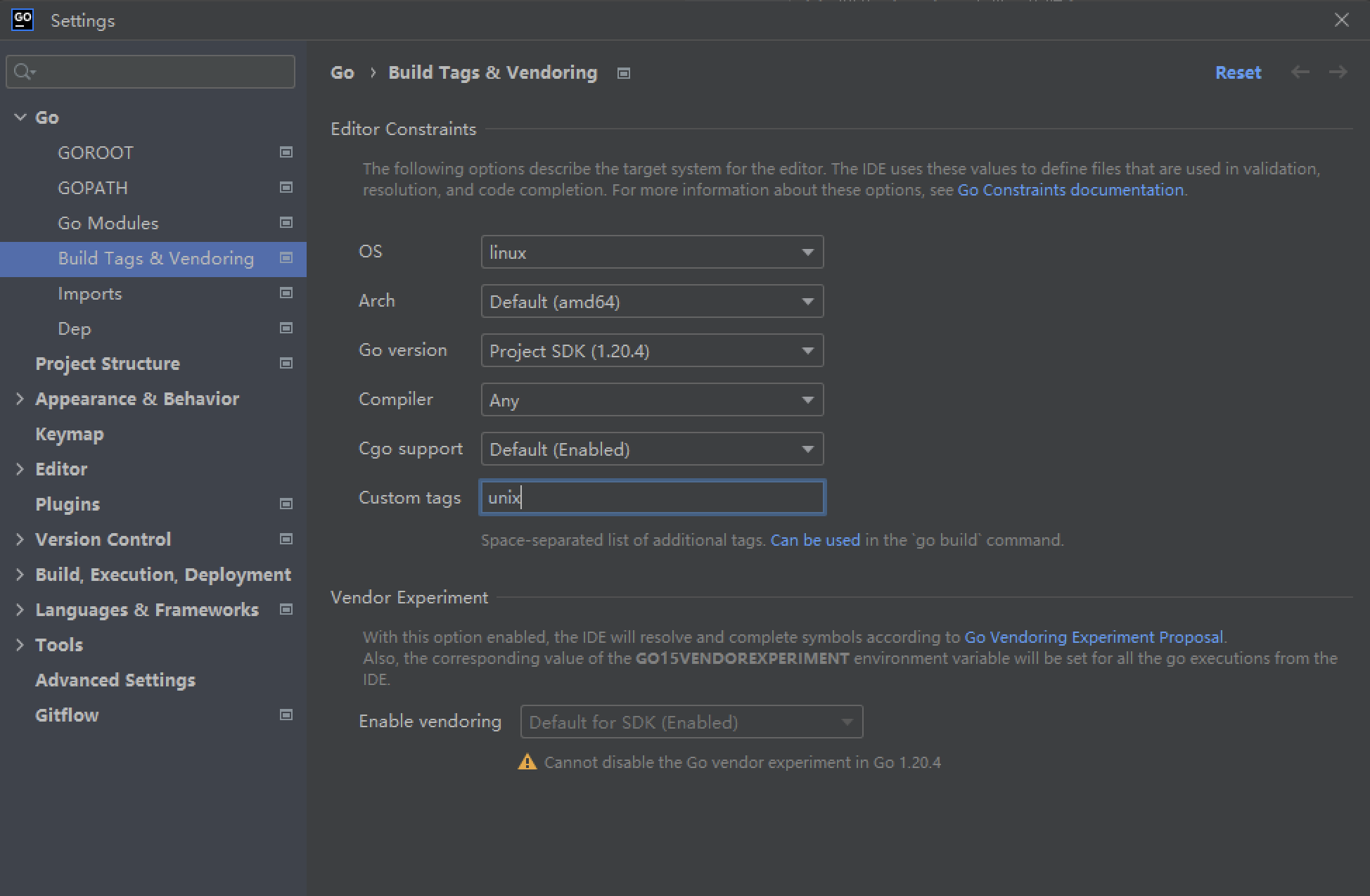
Go 1.19 引入了unix构建标签。因此,需要添加unix到自定义标签.
File -> Settings -> Go -> Build Tags & Vendoring -> Custom tags -> 添加值 “unix”
Goland -> Preferences g-> Go -> Build Tags & Vendoring -> Custom tags -> 添加值 “unix”
Go常用的一些...
// 生成 6 位随机数
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("%06v", rand.New(rand.NewSource(time.Now().UnixNano())).Int31n(1000000)))
// 生成 8 位随机数
fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("%08v", rand.New(rand.NewSource(time.Now().UnixNano())).Int31n(100000000)))
// 设置随机数种子
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
// 生成 6 位随机数
randomNum := rand.Intn(900000) + 100000
fmt.Println(randomNum)
基于golang的手机号格式验证和邮箱格式验证(正则表达式)
//email verify
func VerifyEmailFormat(email string) bool {
//pattern := `\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*` //匹配电子邮箱
pattern := `^[0-9a-z][_.0-9a-z-]{0,31}@([0-9a-z][0-9a-z-]{0,30}[0-9a-z]\.){1,4}[a-z]{2,4}$`
reg := regexp.MustCompile(pattern)
return reg.MatchString(email)
}
//mobile verify
func VerifyMobileFormat(mobileNum string) bool {
regular := "^((13[0-9])|(14[5,7])|(15[0-3,5-9])|(17[0,3,5-8])|(18[0-9])|166|198|199|(147))\\d{8}$"
reg := regexp.MustCompile(regular)
return reg.MatchString(mobileNum)
}
知识扩展:
正则引擎主要可以分为两大类:
- 一种是DFA,
- 一种是NFA。 这两种引擎都有了很久的历史(至今二十多年),当中也由这两种引擎产生了很多变体!于是POSIX的出台规避了不必要变体的继续产生。这样一来,主流的正则引擎又分为3类:
- 一、DFA,
- 二、传统型NFA,
- 三、POSIX NFA。
常用的正则表达式
用户名: /^[a-z0-9_-]{3,16}$/
密码: /^[a-z0-9_-]{6,18}$/
十六进制值: /^#?([a-f0-9]{6}|[a-f0-9]{3})$/
电子邮箱 : /^([a-z0-9_\.-]+)@([\da-z\.-]+)\.([a-z\.]{2,6})$/
/^[a-z\d]+(\.[a-z\d]+)*@([\da-z](-[\da-z])?)+(\.{1,2}[a-z]+)+$/
URL: /^(https?:\/\/)?([\da-z\.-]+)\.([a-z\.]{2,6})([\/\w \.-]*)*\/?$/
IP 地址: /((2[0-4]\d|25[0-5]|[01]?\d\d?)\.){3}(2[0-4]\d|25[0-5]|[01]?\d\d?)/
/^(?:(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.){3}(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)$/
HTML 标签: /^<([a-z]+)([^<]+)*(?:>(.*)<\/\1>|\s+\/>)$/
删除代码\\注释: (?<!http:|\S)//.*$
Unicode编码中的汉字范围: /^[\u2E80-\u9FFF]+$/
go fmt.sprintf 格式化输出
| 动 词 | 功 能 | 字符 | 整型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| %v | 1按值的本来值输出 | 你好-hello | 350 |
| %+v | 在 %v 基础上,对结构体字段名和值进行展开 | 你好-hello | 350 |
| %#v | 输出 Go 语言语法格式的值 | "你好-hello" | 350 |
| %T | 输出 Go 语言语法格式的类型和值 | string | int |
| %% | 输出 % 本体 | % %!(EXTRA string=你好-hello) | % %!(EXTRA int=350) |
| %b | 整型以二进制方式显示 | %!b(string=你好-hello) | 101011110 |
| %o | 整型以八进制方式显示 | %!o(string=你好-hello) | 536 |
| %d | 整型以十进制方式显示 | %!d(string=你好-hello) | 350 |
| %x | 整型以十六进制方式显示 | e4bda0e5a5bd2d68656c6c6f | 15e |
| %X | 整型以十六进制、字母大写方式显示 | E4BDA0E5A5BD2D68656C6C6F | 15E |
| %U | Unicode 字符 | %!u(string=你好-hello) | %!u(int=350) |
| %f | 浮点数 | %!f(string=你好-hello) | %!f(int=350) |
| %p | 指针,十六进制方式显示 | %!p(string=你好-hello) | %!p(int=350) |
| %s | 输出变量本来的值 | 你好-hello | 350 |
go mod
# go mod 初始化
go mod init 模块名
# go mod 下载到本地Cache
go mod download
# go mod 清理本地Cache
go clean -modcache
# go mod 编辑go.mod文件:更多go mod查看 `go help mod edit`
go mod edit
# go mod 打印依赖图
go mod graph
# go mod 删除错误或者不使用的modules
go mod tidy
# go mod 生成vendor目录
go mod vendor
# go mod 验证依赖是否正确
go mod verify
# go mod 查找依赖
go mod why
# go mod 更新依赖到最新版本
go get -u github.com/golang/protobuf
# go mod 更新到指定版本
go get -u github.com/golang/protobuf@指定版本
# go mod 查看有哪些版本
go list -m -versions github.com/golang/protobuf
# go mod 替换包源
go mod edit -replace=golang.org/x/crypto@v0.0.0=github.com/golang/crypto@latest
go mod edit -replace=golang.org/x/sys@v0.0.0=github.com/golang/sys@latest
各种类型转换
1 uint to string
num := uint(123)
// 使用fmt.Sprintf
str1 := fmt.Sprintf("%d", num)
fmt.Println(str1)
// 使用strconv.FormatUint
str2 := strconv.FormatUint(uint64(num), 10)
fmt.Println(str2)
// 使用strconv.Itoa (仅适用于uint类型的32位整数)
str3 := strconv.Itoa(int(num))
fmt.Println(str3)
2 float to string
f := 123.456
s := fmt.Sprintf("%f", f)
fmt.Println(s) // 输出: 123.456000
f := 123.456
s := strconv.FormatFloat(f, 'f', -1, 64)
fmt.Println(s) // 输出: 123.456000
3 string to float
str := "123.456"
floatValue, err := strconv.ParseFloat(str, 64)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("转换错误: %v\n", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("转换后的浮点数: %f\n", floatValue)
4 string to uint
str := "12345"
num, err := strconv.ParseUint(str, 10, 32) // 第二个参数是基数(这里是十进制),第三个参数是位大小(32位系统中用uint32表示)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("转换出错: %v\n", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("转换后的数字是: %d\n", num)
interface to string
func Strval(value interface{}) string {
// interface 转 string
var key string
if value == nil {
return key
}
switch value.(type) {
case float64:
ft := value.(float64)
key = strconv.FormatFloat(ft, 'f', -1, 64)
case float32:
ft := value.(float32)
key = strconv.FormatFloat(float64(ft), 'f', -1, 64)
case int:
it := value.(int)
key = strconv.Itoa(it)
case uint:
it := value.(uint)
key = strconv.Itoa(int(it))
case int8:
it := value.(int8)
key = strconv.Itoa(int(it))
case uint8:
it := value.(uint8)
key = strconv.Itoa(int(it))
case int16:
it := value.(int16)
key = strconv.Itoa(int(it))
case uint16:
it := value.(uint16)
key = strconv.Itoa(int(it))
case int32:
it := value.(int32)
key = strconv.Itoa(int(it))
case uint32:
it := value.(uint32)
key = strconv.Itoa(int(it))
case int64:
it := value.(int64)
key = strconv.FormatInt(it, 10)
case uint64:
it := value.(uint64)
key = strconv.FormatUint(it, 10)
case string:
key = value.(string)
case []byte:
key = string(value.([]byte))
default:
newValue, _ := json.Marshal(value)
key = string(newValue)
}
return key
}
map 接受不知道结构的 json 数据
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(c.Request.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
defer c.Request.Body.Close()
var payload map[string]interface{}
if err := json.Unmarshal(body, &payload); err != nil {
log.Println(err)
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
判断map key
value, ok := myMap[key]
if ok {
// key存在,进行相关操作
} else {
// key不存在
}